Water-based light-curable coating instead of diluted monomer with water, eliminating the irritation of the monomer on the skin, but also more secure, easy to clean equipment to overcome the bulk of the dilute monomer polymerization shrinkage problems, and easy to control coating viscosity. However, it also has some problems that are related to the volatility of water. It is difficult to solve the problem. The first step is to remove the water before lighting, so it is necessary to add drying equipment and consume energy. The resulting film has a low gloss, sensitivity to water, and relatively poor wash durability. Water-based photocurable coatings are now only suitable for substrates that are prone to absorb water, such as paper and wood.
Water-based light-curing coatings can also be divided into two major categories, one is an emulsion type and the other is a water-reducing type. The former can be prepared by a mechanical emulsification method, and for the general resin, an emulsifier and a protective colloid are added. For some resins with hydrophilic groups or modified resins, they are easily emulsified or self-emulsifiable. Water-based photocurable resins can also be prepared by a method similar to that of ordinary water-reducible resins by introducing a carboxyl group or an amine group on the prepolymer, followed by neutralization and dilution with water. Photoinitiators in waterborne photocurable coatings can be photoinitiators or derivatives that introduce hydrophilic groups. They can be dispersed by emulsifiers. Initiators for waterborne photocurable coatings require low volatility to avoid escape during heating.
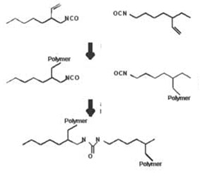
Light curing/moisture curing
Hybrid and dual light curing system
The hybrid and dual photocurable system refers to a curing system that includes two different curing reaction types. The two curing reactions occur at the same time called the hybrid photocuring system. The two curing reactions are called the double curing system.
â—†Hybrid curing system
Free radical-cationic hybrid photocuring systems are typical and are also practical hybrid photocuring systems. For example, there are photosensitive polymerization systems of acrylates/epoxides or mixed monomers or oligomers of acrylate/vinyl ether. This mixed system can increase the depth of cure and speed of cure, and can have more monomer available. The choice is used to adjust the viscosity and hardness of the final product, softness, adhesion and so on. For example, when the cyclic monomer is subjected to cationic ring-opening polymerization, there is little volume change, and sometimes there may also be swelling. On the contrary, when the acrylate polymerizes, the shrinkage is very severe, resulting in internal stress. Therefore, the introduction of epoxy compounds in the acrylate system can be balanced. Acrylic volume change; free radical-cation hybrid photocuring system can effectively improve the mechanical properties and solvent resistance of cured products. On the other hand, due to the presence of basic impurities in the system, the induction period of cationic polymerization is generally longer, but free radicals can provide rapid polymerization, while the cations are long-lived, and after light irradiation, dark polymerization can continue, radicals It quickly disappears, so cationic polymerization can compensate for insufficient photocuring. In practical applications, there are usually two initiators in radical-cation hybrid photocuring systems that initiate radical polymerization and cationic polymerization, respectively. The cationic initiator diphenyl iodide salt usually needs the sensitizer in use, but in the hybrid system, the free radical photoinitiator can precisely sensitize the salt without additional sensitizer.
â—† Dual curing system
For some components, no matter how the curing device and the light source are designed, there are always some areas where the light cannot be achieved or the light intensity is insufficient. Therefore, a pure photo-curable coating cannot meet the requirements. In order to solve this problem, hybrid or dual-curing systems in which photocuring and thermal curing occur simultaneously or sequentially have been developed. In general, dual curing is performed first with photocuring followed by other curing reactions. Although the dual curing has lost the advantages of fast photo-curing coating, it still has some advantages: Since most of the objects have been dried in the light, the coating sag is prevented, and subsequent operations are also facilitated, reducing the number of objects Possibility of contamination. The curing temperature of the post-cure reaction in the system is generally designed to be lower and the curing time is shorter.
There are different types of methods for dual-cure coatings. For example, a dual curing system consisting of an acrylated polyurethane with isocyanate groups and a polyol with double bonds is a combination of photo-curing and hydroxyl-isocyanate group condensation reactions. as follows:
As another example, acrylated polyurethanes with isocyanate groups are sequentially photocured and moisture cured. The response is expressed as follows:
3D light curing equipment and technology
When three-dimensional (3D) parts of different shapes and sizes, angles, bends, edges, and irregularities are light-cured, it is necessary to have light projected onto all the surfaces, and to have reliable and sufficient energy. In order to obtain full cure of the entire surface, some measures need to be taken, such as designing the production line according to the size and shape of the object, whether the object is vertical or horizontal, and whether the potential shadow can be illuminated by rotation or the like. In order to perform the light curing energy requirement and the adjustment of the curing speed, it is an important method to mount the light source on the robot. The use of robots has many advantages. Many parts that cannot be illuminated by fixed light sources can be effectively illuminated. The development of three-dimensional coating and curing devices that require a large space is an important issue for the use of photocurable coatings on automobiles or other large-scale devices.
New light curing coating
Research on photo-induced alkaline production has made great progress. Based on this, it is expected to develop new anionic photocuring systems, including amine-cured epoxy coatings. There is room for further development of free radical photo-curing and cationic curing coatings, such as thiol-ene radical photocuring coatings and acid-catalyzed polycondensation photocurable coatings.
Extracted from <Paints and Inks>
From the Department of Chemistry of Tsinghua University
1. Work chair: This is the most common type of office chair designed for use on a desk or computer. They usually have adjustable height, backrest, and armrests, and are usually mounted on wheels for easy movement.
2. Executive chair: These chairs are larger and more luxurious than task chairs, with higher backrests and more padding. They are usually made of leather and have more advanced functions such as tilting and tilting. Suitable for high-level personnel in various offices.
3. Conference chair: These chairs are designed for use in conference rooms and are usually lighter and more stackable than other office chairs, making it easier to decorate the venue. They may have adopted a more minimalist design and come with a writing pad.
Mesh Chair,Pu Chair,Leather Chair,Boss Chair
Foshan Shengshi Zhihui Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.sshotelfurniture.com