The map is a special type of print. It has a very important role in the country's economy, national defense, culture, and education. In recent years, due to the combination of digital mapping technology and electronic publishing technology, the map publishing field has undergone earth-shaking changes. The quality and production efficiency of the map have been greatly improved. Traditional map mapping and publishing operations have been digitized map production. Mode replaced.
First, the characteristics of map printing
Compared with other prints, the publishing and printing of maps has its own characteristics, mainly including:
1. Large print format
The size of the map can not be arbitrarily divided by human, either according to the specification, or by the designer in the map compilation design. For example, according to the specification, topographic maps are to be divided by latitude and longitude, and the map size is about 60×44 cm, including the decoration outside of the map. Therefore, the print size of the topographic map has reached 75×54 cm. If it is a wall chart, the format of the canvas will be even bigger: some will be stitched together with a few sheets or more than a dozen sheets of paper. For example, the 1:2.5 million "Full Map of China" is made up of 9 pieces of full-open paper. It is a feature that other prints do not have.
2. High copying accuracy
In the application, maps are sometimes obtained through topographical maps or other maps to obtain data. Therefore, the size of maps must be within the allowable error range for the copied and copied maps; the lines and symbols must conform to the specifications. Or design rules; must ensure that the map contents between two adjacent maps can be correctly stitched. In short, the geometrical accuracy of the map cannot be affected by print copying.
3. Print color maps with monochrome originals
Most of the maps provided for publication and printing are monochromatic manuscripts. During the printing process, workers are required to refer to the provided monochrome manuscripts, and the plates are printed into color maps. Therefore, many processes are added to the printing platemaking process. difficult.
4. Printing color
Although the map is monochrome, it is inconvenient to use. Most of the maps are now printed in color. Prior to 1964, for large-scale topographic maps, the schema rules were printed in 8 colors: black, brown, dark blue, medium blue, light blue, orange, earth yellow, and green; after 1964, black, brown, blue, and Printed in 4 colors such as green. The national standard specifies that the 1:500,000 topographic map be printed in 6 colors; the 1:1 million topographic map should be printed in 9 colors; and the aeronautical map should be printed in 14 colors. Common maps, thematic maps, geological maps, mineral maps, etc. use more color, 1975 version 1:500 million "Asia Geological Map" with up to 40 colors.
Today's map printing generally uses four kinds of inks such as yellow, magenta, cyan and black, but there are some special requirements for map printing that must also include other special printing colors such as purple and brown.
5. It must be able to repair the mistakes in time in the printing and publishing operations
This is because the contents of the map are very complex and represent a certain amount of content from one point to another. Therefore, it will inevitably lead to individual errors in the process of plate making. This will require correcting and repairing the map on the film or plate in a timely manner.
Second, the traditional map drawing and publishing process
Since lithography uses photolithography, which facilitates changing the scale and satisfies the requirements for map printing, the traditional cartographic drawing and publishing is entirely based on manual lithographic printing. The basic process flow is shown in Figure 1.
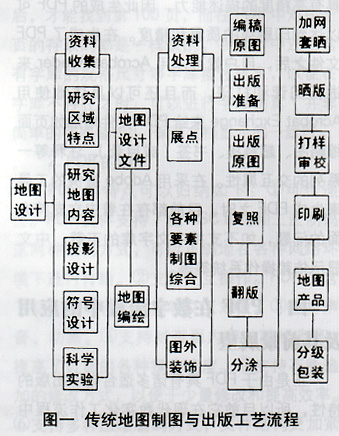
From the above figure, we can see that in the traditional map drawing and publishing process, from the overall design to the map's copy printing, each step appears in the form of logistics, and every process of production is inseparable from the Artificial participation and operation. This kind of production process is time consuming, time-consuming and cumbersome. At the same time, due to such a production process, both the first production and the later editions make it very difficult for the editors to revise their work. The quality of the products is also affected by the factors of the operators.
(to be continued)

What is infill on artificial turf?
Tpe Grass Infill normally refers to the products that are placed in between the blades or fibers of artificial turf, or the synthetic grass blades. The purpose of infill as mentioned above is to help the grass blades stand up, or return back to their intended upright position after they have been exposed to pressure.
Tpe Grass Infill,Tpe Turf Infill,Tpe Sand For Artificial Turf,Tpe Sand For Artificial Grass
JIANGSU WMGRASS CO., LTD. , https://www.wmgrasslawns.com